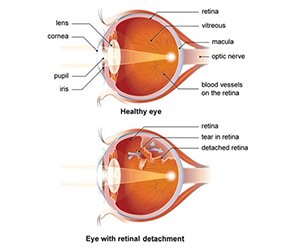
What is retinal detachment?
The retina is a light-sensitive membrane located at the back of the eye. When light passes through your eye, the lens focuses an image on your retina. The retina converts the image to signals that it sends to your brain through the optic nerve. The retina works with the cornea, lens, and other parts of your eye and brain to produce normal vision.
Retinal detachment occurs when the retina separates from the back of your eye. This causes loss of vision that can be partial or total, depending on how much of the retina is detached. When your retina becomes detached, its cells may be seriously deprived of oxygen. Retinal detachment is a medical emergency. Call your doctor right away if you suffer any sudden vision changes.
There’s a risk of permanent vision loss if retinal detachment is left untreated or if treatment is delayed.
SYMPTOMS
Symptoms
Retinal detachment itself is painless. But warning signs almost always appear before it occurs or has advanced, such as:
- The sudden appearance of many floaters — tiny specks that seem to drift through your field of vision
- Flashes of light in one or both eyes
- Blurred vision
- Gradually reduced side (peripheral) vision
- A curtain-like shadow over your visual field
Causes
Retinal detachment can occur as a result of:
- A sagging vitreous (VIT-ree-us) — the gel-like material that fills the inside of your eye
- Injury
- Advanced diabetes
Diagnosis:
- Retinal examination.The doctor may use an instrument with a bright light and a special lens (ophthalmoscope) to examine the back of your eye, including the retina. The ophthalmoscope provides a highly detailed view, allowing the doctor to see any retinal holes, tears or detachments.
- Ultrasound imaging.Your doctor may use this test if bleeding has occurred in the eye, making it difficult to see your retina.
Treatment
- Laser surgery (photocoagulation).The surgeon directs a laser beam into the eye through the pupil. The laser makes burns around the retinal tear, creating scarring that usually "welds" the retina to underlying tissue.
- Freezing (cryopexy).After giving you a local anesthetic to numb your eye, the surgeon applies a freezing probe to the outer surface of the eye directly over the tear. The freezing causes a scar that helps secure the retina to the eye wall.