Diabetic retinopathy is the most common form of diabetic eye disease. Diabetic retinopathy usually only affects people who have had diabetes (diagnosed or undiagnosed) for a significant number of years.
Retinopathy can affect all diabetics and becomes particularly dangerous, increasing the risk of blindness, if it is left untreated.
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common form of diabetic eye disease. Diabetic retinopathy usually only affects people who have had diabetes (diagnosed or undiagnosed) for a significant number of years.
Retinopathy can affect all diabetics and becomes particularly dangerous, increasing the risk of blindness, if it is left untreated.
The risk of developing diabetic retinopathy is known to increase with age as well with less well controlled blood sugar and blood pressure level.
What is diabetic retinopathy?
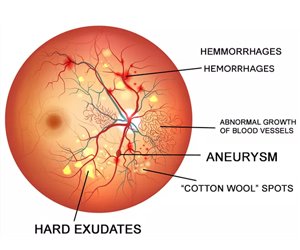
Diabetic retinopathy occurs when changes in blood glucose levels cause changes in retinal blood vessels. In some cases, these vessels will swell up (macular oedema) and leak fluid into the rear of the eye.
In other cases, abnormal blood vessels will grow on the surface of the retina.
Unless treated, diabetic retinopathy can gradually become more serious and progress from ‘background retinopathy’ to seriously affecting vision and can lead to blindness.
Diabetic retinopathy includes 3 different types:
- Background Retinopathy
- Diabetic Maculopathy
- Proliferative Retinopathy
What are the symptoms of diabetic retinopathy?
Like many conditions of this nature, the early stages of diabetic retinopathy may occur without symptoms and without pain. An actual influence on the vision will not occur until the disease advances.
Macular oedema can result from maculopathy and affect vision occurs if leaking fluid causes the macular to swell. New vessels on the retina can prompt bleeding, which can also block vision in some cases.
Symptoms may only become noticeable once the disease advances, but the typical symptoms of retinopathy to look out for include:
- Sudden changes in vision / blurred vision
- Eye floaters and spots
- Double vision
- Eye pain